Property FontSize
- Namespace
- BitMiracle.Docotic.Pdf
- Assembly
- BitMiracle.Docotic.Pdf.dll
FontSize
Gets the scale factor of the font used to draw this chunk.
public double FontSize { get; }Property Value
- double
The scale factor of the font used to draw this chunk.
Remarks
A font defines the glyphs for one standard size. This standard is arranged so that the nominal height of tightly spaced lines of text is 1 unit. In the default user coordinate system, this means the standard glyph size is 1 point (or 1 ⁄ 72 inch). The standard-size font must then be scaled to be usable.
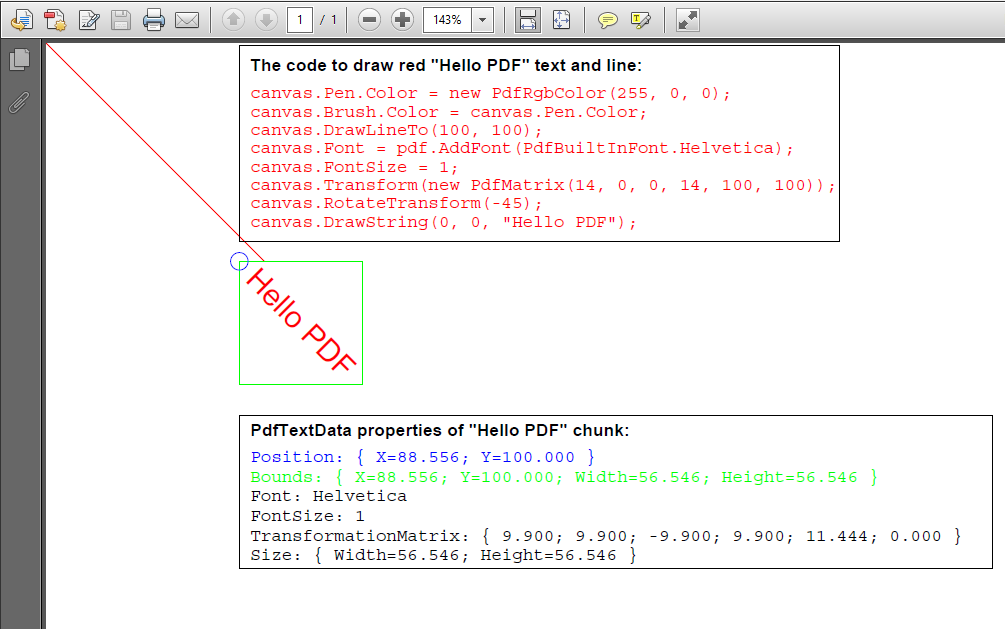
This property retrieves the scale factor used to draw the text chunk. Usually, the FontSize property retrieves values like 10, 12, 14. But the FontSize might have an arbitrary value like 1, 1000, -1, -10. It's just a scale factor.
The final height of the text chunk depends on both FontSize and TransformationMatrix properties.
For a non-transformed text the TransformationMatrix is the identity
matrix (the IsIdentity() property is equal
to true). In such a case the absolute text height is equal to
Math.Abs(FontSize).
For a scaled text the TransformationMatrix looks like
{ M11; 0; 0; M22; 0; 0 }. In such a case the absolute text height is equal to
Math.Abs(TransformationMatrix.M22 * FontSize).
For an arbitrarily transformed text the TransformationMatrix
looks like { M11; M12; M21; M22; X; Y }. In such a case the absolute text height is
equal to
(Math.Abs(FontSize) * Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(TransformationMatrix.M21, 2) + Math.Pow(TransformationMatrix.M22, 2))).
Let's try to understand the nature of this formula. At first, the matrix
{ FontSize, 0, 0, FontSize, 0, 0 } is multiplied by the current
TransformationMatrix (current matrix being the right multiplier).
The resulting matrix is { M11 * FontSize; M12 * FontSize; M21 * FontSize; M22 * FontSize; X; Y }.
Then we calculate the text height in the new transformed space. We map points (0; 0)
and (0; 1) from default space to the transformed space. The result is (X; Y)
and (M21 * FontSize + X; M22 * FontSize + Y), respectively. And finally we
calculate the length of this vector, that is exactly the absolute text height in the
transformed space:
Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(M21 * FontSize, 2) + Math.Pow(M22 * FontSize, 2)) =
Math.Abs(FontSize) * Math.Sqrt(Math.Pow(M21, 2) + Math.Pow(M22, 2)).
Below is an example of rotated text for which the FontSize is equal to 1.
- See Also